What Really Causes Acne? Myths, Types & Solutions You Need to Know!
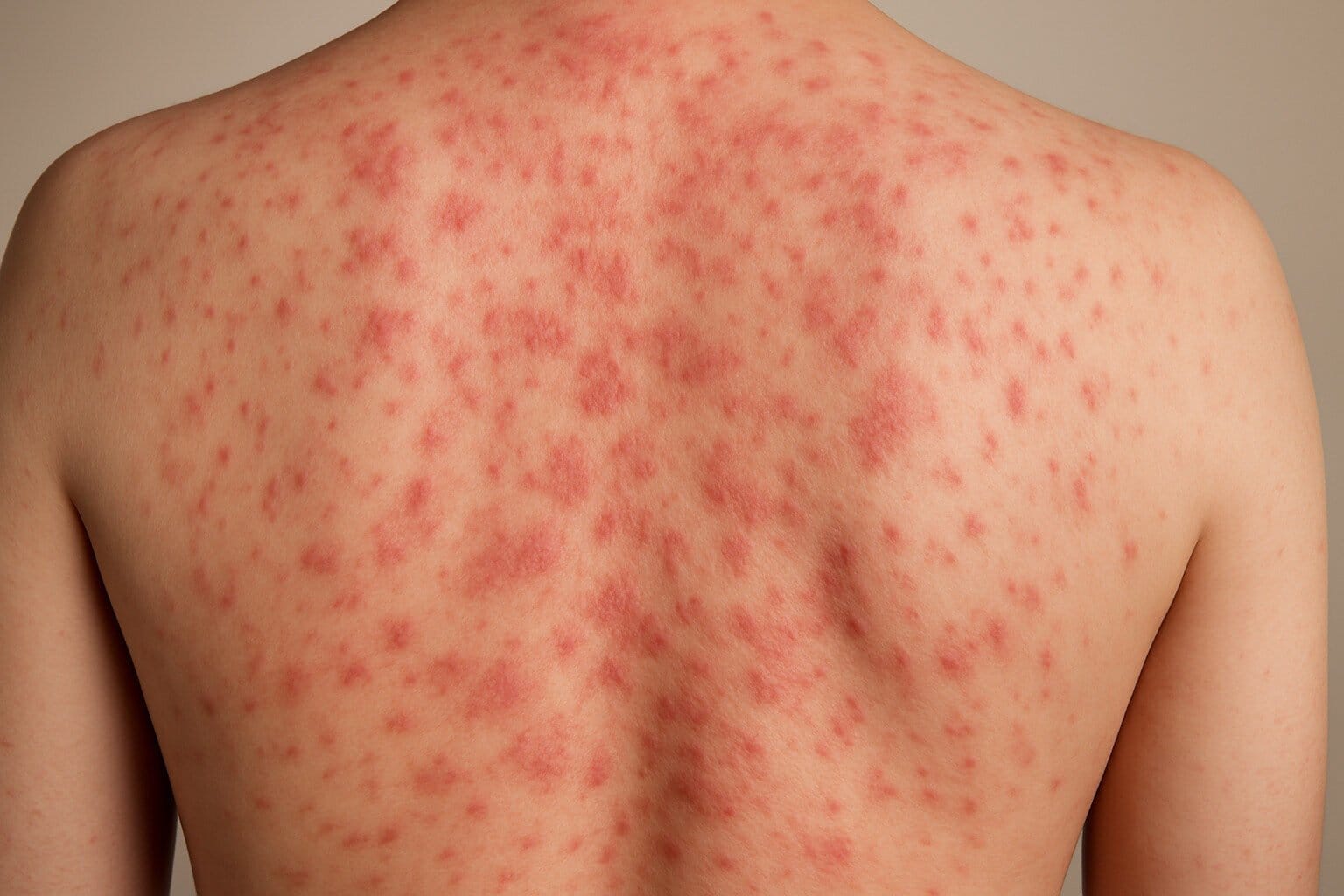
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions worldwide. It appears as pimples, blackheads, and cysts, mostly on oily areas like the face, back, and shoulders. These breakouts happen when hair follicles get clogged with oil and dead skin cells, creating a perfect breeding ground for bacteria.
Although acne is often tied to puberty, it can affect people of all ages — from teens to adults in their 30s and even 40s. In fact:
- 85% of people between 12 to 24 will experience acne.
- 40% of adults in their 20s still face acne breakouts.
- 15% of people in their 30s also report persistent acne.
Beyond the physical impact, acne can leave emotional scars. The visible nature of breakouts often leads to low self-esteem, social anxiety, and even depression. That’s why understanding acne is about more than just skincare — it’s about well-being and confidence.
Let’s explore what causes acne, how to spot the different types, and what you can do to treat and prevent it effectively.
Why Acne Happens?
Acne is triggered by a mix of internal and external factors, making it a complex condition to tackle.
Hormonal Changes
- Puberty, menstruation, and stress can cause hormonal spikes.
- These hormones signal oil glands to produce excess sebum, which clogs pores.
Bacterial Growth
- Propionibacterium acnes thrives in clogged follicles.
- This triggers the inflammatory response, leading to red, swollen bumps.
Diet & Nutrition
- High-glycemic foods (like white bread and sugar) can spike insulin and worsen acne.
- Some people are sensitive to dairy, which may lead to more breakouts.
Environmental Factors
- Pollution can increase inflammation.
- Humidity triggers more oil production.
Understanding these root causes helps you choose the right treatment — because not all acne is created equal.
Types of Acne & How To Diagnose Yours?
There are several kinds of acne, and recognizing which type you have is key to choosing the right remedy.
| Type | Appearance | Severity | Inflammatory? |
| Whiteheads | Small, flesh-colored bumps | Mild | No |
| Blackheads | Open pores with dark tips | Mild | No |
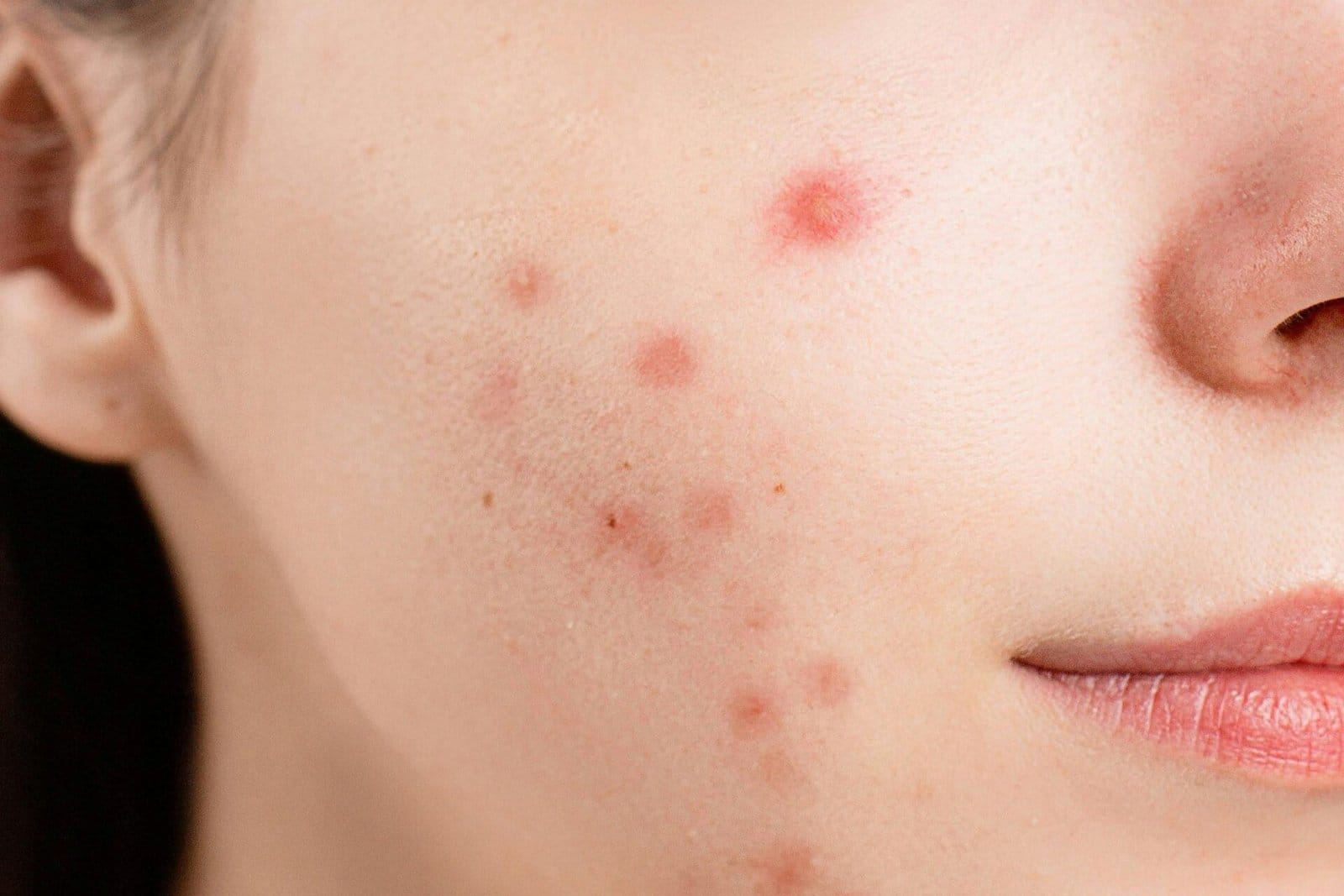
| Papules | Red, raised bumps | Moderate | Yes |
| Pustules | Pimples with white or yellow pus | Moderate | Yes |
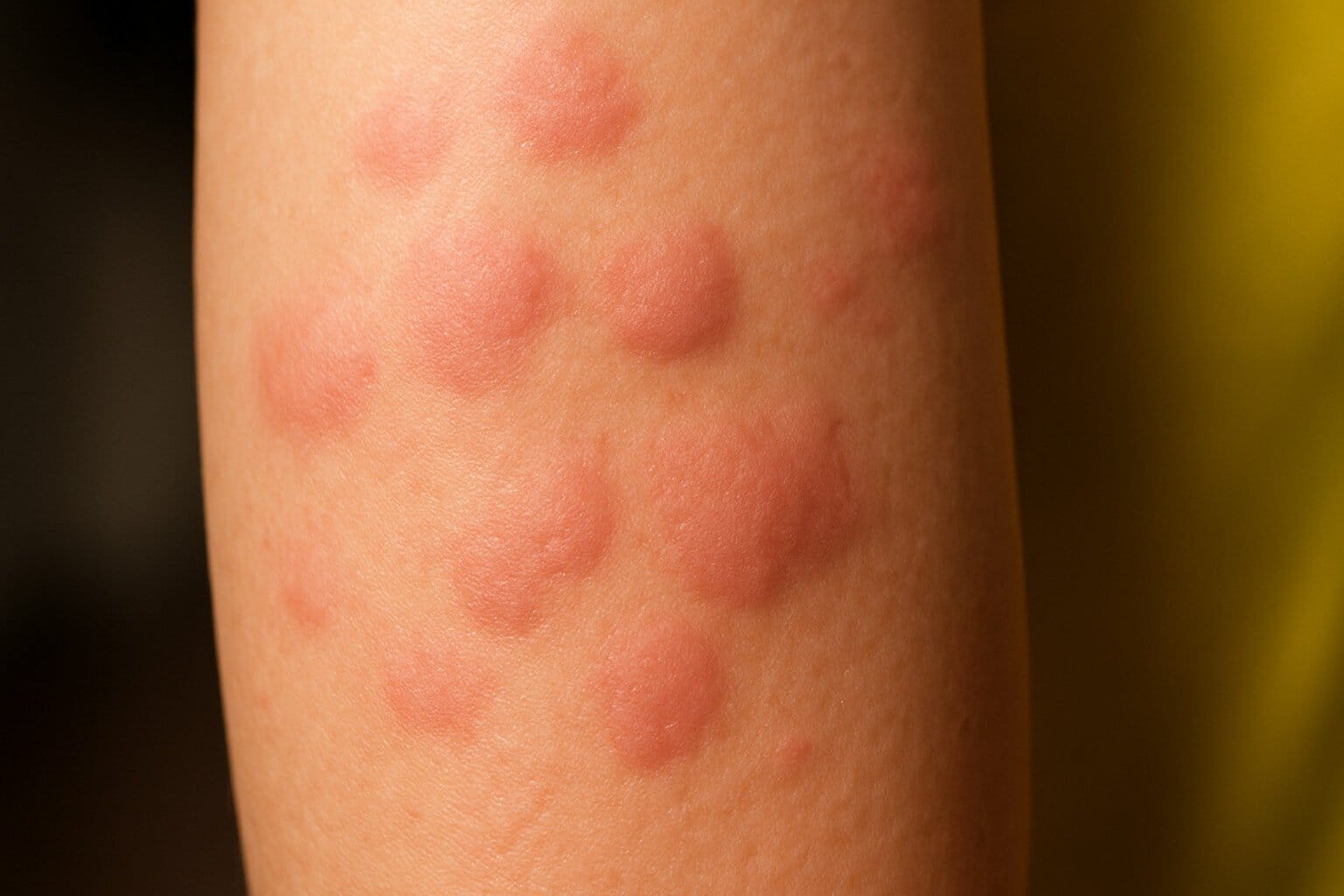
| Nodules | Hard, painful lumps under the skin | Severe | Yes |
| Cysts | Large, soft lumps filled with pus | Severe (scarring) | Yes |
Tip: If you’re dealing with painful, persistent, or scarring acne, a dermatologist can help with a diagnosis and prescription treatment.
Debunking Common Acne Myths
Let’s bust some of the biggest acne myths that can actually make things worse:
Myth 1: Acne means Poor Hygiene
Truth: Washing your face too much can strip natural oils and irritate the skin.
Myth 2: Chocolate and Greasy Foods Cause Acne
Truth: While diet plays a role, high-glycemic foods and dairy are more likely culprits.
Myth 3: Only Teens Get Acne
Truth: Adults especially women can get acne well into their 30s and 40s due to stress and hormones.
Myth 4: Tanning Clears Up Acne
Truth: Sun exposure may temporarily dry pimples, but it damages skin and can worsen breakouts in the long run.
Understanding the facts helps you make smart, evidence-based choices for your skin.
Solutions and Preventions for Acne
Here’s a breakdown of science-backed acne treatments and how to prevent future breakouts:
Over-the-Counter Products
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills bacteria.
- Salicylic Acid: Unclogs pores.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): Exfoliate dead skin.
Prescription Options
- Topical Retinoids: Promote skin cell turnover.
- Oral Antibiotics: Reduce inflammation.
- Hormonal Treatments: Especially useful for adult women.
Always consult a dermatologist before starting prescription treatments.
Natural Remedies
- Tea Tree Oil: Antibacterial.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes inflammation.
- Green Tea Extract: Reduces oil and redness.
Prevention Tips
- Wash your face gently twice a day.
- Avoid touching your face.
- Change pillowcases weekly.
- Eat more whole foods and reduce sugar intake.
Manage stress with yoga, exercise, or mindfulness.
Recommendations
Below is a list of products that produce effective results against acne:
Neutrogena Oil-Free Acne Wash (Salicylic Acid 2%) – A classic daily cleanser that helps control breakouts effectively.
Neutrogena Rapid Clear Stubborn Acne Spot Gel (Benzoyl Peroxide 10%) – Fast-acting treatment for reducing redness and inflammation in stubborn acne.
Cefaclor Duo (+) Acne Treatment – Combines niacinamide, salicylic acid, and LHA to treat various acne types and smooth skin texture.
Effaclar Purifying Foaming Gel – Gentle foaming cleanser, perfect for oily and acne-prone skin.
CeraVe Acne Foaming Cream Cleanser (Benzoyl Peroxide 4%) – A gentle yet powerful daily wash to fight acne without over-drying.
CeraVe Resurfacing Retinol Serum – Helps fade post-acne marks and prevents future breakouts.
The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% – Reduces redness, controls sebum, and supports acne prevention.
The Ordinary Salicylic Acid 2% Solution – Targets clogged pores and gently exfoliates the skin.
Garnier Pure Active Anti-Acne White Foam – Budget-friendly daily cleanser that controls oil and prevents breakouts.
Garnier Pure Active Serum – Lightweight formula with salicylic acid and niacinamide for balanced, clear skin.
Nivea Derma Skin Clear Wash Gel – Salicylic acid-powered cleanser for purifying and refreshing the skin.
Nivea Perfect & Radiant 3-in-1 Cleanser – Multi-tasking cleanser that handles mild acne and brightens skin tone.
Clean & Clear Advantage Acne Spot Treatment – Effective spot treatment to quickly reduce pimples.
Clean & Clear Essentials Foaming Facial Cleanser – Teen-friendly daily face wash that’s both gentle and effective.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Does acne go away on its own?
Mild acne can fade with time, especially after puberty, but moderate to severe acne often requires treatment.
2. Can stress really cause acne?
Yes. Stress increases cortisol, which can lead to hormonal imbalances and more oil production.
3. Are natural remedies effective for acne?
They can help mild acne, but for severe cases, professional treatment is usually needed.
4. Is it okay to pop pimples?
No. Popping pimples can worsen inflammation and lead to scarring.
5. What skincare routine is best for acne-prone skin?
Gentle cleansing, non-comedogenic moisturizers, and spot treatments with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide.
6. Can drinking more water help acne?
While hydration is great for overall skin health, water alone won’t clear acne but it helps support healing.
Subscribe to our newsletter!